Implementing Bahdanau Attention in a RNN(seq2seq)
Posted on * • 15 minutes • 3089 words
Bahdanau Attention is a mechanism used in sequence-to-sequence models, particularly in neural machine translation tasks, to help the model focus on relevant parts of the input sequence when generating each part of the output sequence. It was introduced by Dzmitry Bahdanau, Kyunghyun Cho, and Yoshua Bengio in their paper “Neural Machine Translation by Jointly Learning to Align and Translate” in 2014.
In traditional sequence-to-sequence models, such as those based on Recurrent Neural Networks (RNNs) or Long Short-Term Memory (LSTM) networks, a fixed-length context vector is used to summarize the entire input sequence. However, this fixed-length representation may not capture all the relevant information, especially in longer sequences.
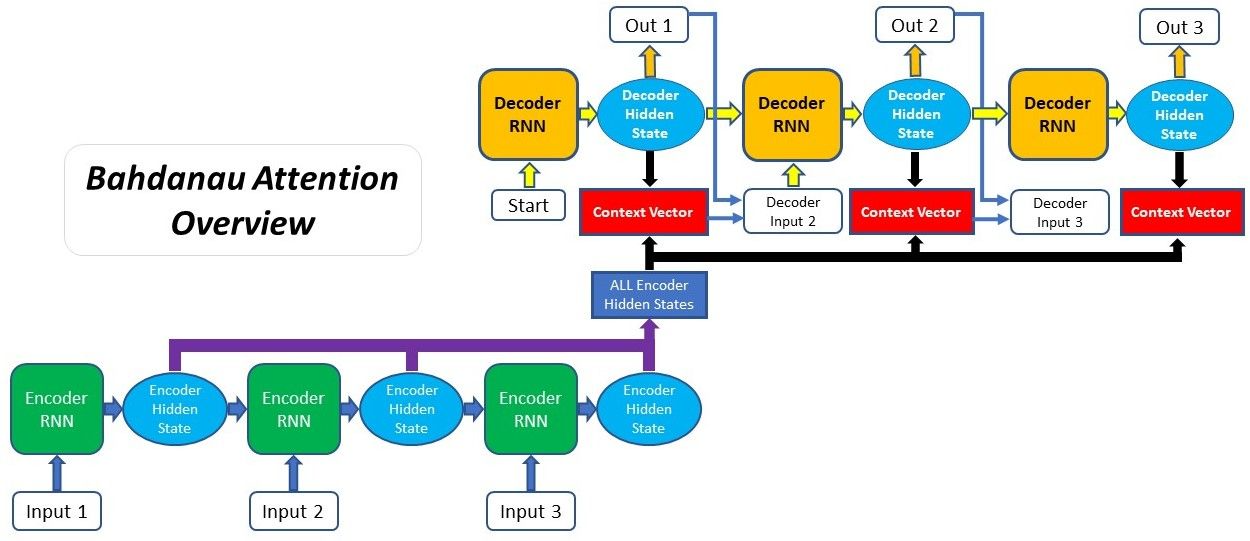
Bahdanau Attention addresses this issue by allowing the model to dynamically focus on different parts of the input sequence as it generates each output token. It does this by computing attention weights for each input token, indicating how much attention the model should pay to that token when generating the current output token.
 source: https://blog.floydhub.com/attention-mechanism/
source: https://blog.floydhub.com/attention-mechanism/
The attention mechanism typically involves the following steps:
- Score Calculation: A score is calculated for each pair of input and output positions. This score indicates the relevance of the input position to the output position being generated. Softmax: The scores are passed through a softmax function to obtain attention weights, ensuring that the weights sum up to 1 and represent a probability distribution over the input positions.
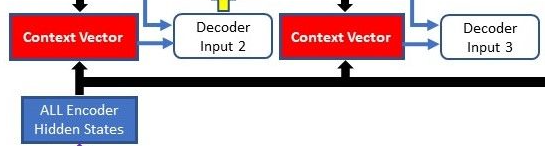
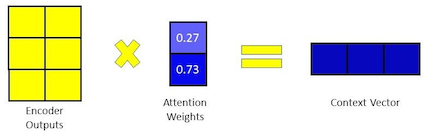
- Weighted Sum: The input sequence is then weighted by these attention weights, and the weighted sum is computed. This gives a context vector, which captures the relevant information from the input sequence for generating the current output token.
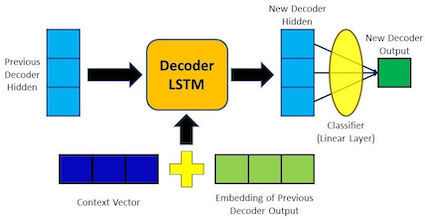
- Context Vector: The context vector is concatenated with the output of the previous decoder timestep (or otherwise combined with it) and passed through the decoder network to generate the next output token.
- Bahdanau Attention allows the model to focus on different parts of the input sequence based on the context of the current decoding step. This attention mechanism has been widely adopted in various sequence-to-sequence tasks, improving the performance of neural machine translation models and other related tasks.
!pip3 install Cython
Requirement already satisfied: Cython in /usr/local/lib/python3.10/dist-packages (3.0.8)
# Importing....
import numpy as np
import torch
from torch import nn
from torch.nn import functional as F
import torch.optim as optim
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import os
import re
import random
device = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")
Encoder Decoder
source: https://www.guru99.com/seq2seq-model.html
Download Data
Download English-French sentence pairs. You can download other language pairs here: http://www.manythings.org/anki/
!wget http://www.manythings.org/anki/fra-eng.zip
!unzip fra-eng.zip
--2024-02-14 12:54:43-- http://www.manythings.org/anki/fra-eng.zip
Resolving www.manythings.org (www.manythings.org)... 173.254.30.110
Connecting to www.manythings.org (www.manythings.org)|173.254.30.110|:80... connected.
HTTP request sent, awaiting response... 200 OK
Length: 7833145 (7.5M) [application/zip]
Saving to: ‘fra-eng.zip’
fra-eng.zip 100%[===================>] 7.47M 4.86MB/s in 1.5s
2024-02-14 12:54:45 (4.86 MB/s) - ‘fra-eng.zip’ saved [7833145/7833145]
Archive: fra-eng.zip
inflating: _about.txt
inflating: fra.txt
Preparing Vocabulary
SOS_token = 0
EOS_token = 1
MAX_LENGTH = 5 # 20
#initialize Lang Class
class Lang:
def __init__(self):
#initialize containers to hold the words and corresponding index
self.word2index = {}
self.word2count = {}
self.index2word = {0: "SOS", 1: "EOS"}
self.n_words = 2 # Count SOS and EOS
# split a sentence into words and add it to the container
def addSentence(self, sentence):
for word in sentence.split(' '):
self.addWord(word)
# If the word is not in the container, the word will be added to it,
# else, update the word counter
def addWord(self, word):
if word not in self.word2index:
self.word2index[word] = self.n_words
self.word2count[word] = 1
self.index2word[self.n_words] = word
self.n_words += 1
else:
self.word2count[word] += 1
Preprocessing
# Normalize every sentence
def normalize_sentence(df, lang):
sentence = df[lang].str.lower()
sentence = sentence.str.replace('[^A-Za-z\s]+', '')
sentence = sentence.str.normalize('NFD')
sentence = sentence.str.encode('ascii', errors='ignore').str.decode('utf-8')
return sentence
def read_sentence(df, lang1, lang2):
sentence1 = normalize_sentence(df, lang1)
sentence2 = normalize_sentence(df, lang2)
return sentence1, sentence2
def read_file(loc, lang1, lang2):
df = pd.read_csv(loc, sep='\t', header=None,
names=[lang1, lang2, 'attribution'])
return df
def process_data(file, lang1,lang2):
df = read_file(file, lang1, lang2)
print("Read %s sentence pairs" % len(df))
sentence1, sentence2 = read_sentence(df, lang1, lang2)
source = Lang()
target = Lang()
pairs = []
for i in range(len(df)):
if len(sentence1[i].split(' ')) < MAX_LENGTH and \
len(sentence2[i].split(' ')) < MAX_LENGTH:
full = [sentence1[i], sentence2[i]]
source.addSentence(sentence1[i])
target.addSentence(sentence2[i])
pairs.append(full)
return source, target, pairs
df = read_file('fra.txt', 'eng', 'fra')
df.head()
| eng | fra | attribution | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | Go. | Va ! | CC-BY 2.0 (France) Attribution: tatoeba.org #2... |
| 1 | Go. | Marche. | CC-BY 2.0 (France) Attribution: tatoeba.org #2... |
| 2 | Go. | En route ! | CC-BY 2.0 (France) Attribution: tatoeba.org #2... |
| 3 | Go. | Bouge ! | CC-BY 2.0 (France) Attribution: tatoeba.org #2... |
| 4 | Hi. | Salut ! | CC-BY 2.0 (France) Attribution: tatoeba.org #5... |
Read and process data
lang1 = 'eng'
lang2 = 'fra'
file = 'fra.txt'
source, target, pairs = process_data(file, lang1, lang2)
randomize = random.choice(pairs)
print('random sentence {}'.format(randomize))
# print number of words
input_size = source.n_words
output_size = target.n_words
print('Input : {}, Output : {}'.format(input_size, output_size))
Read 229803 sentence pairs
<ipython-input-4-97392d032bd8>:4: FutureWarning: The default value of regex will change from True to False in a future version.
sentence = sentence.str.replace('[^A-Za-z\s]+', '')
random sentence ['thats important to me', 'cest important pour moi']
Input : 6412, Output : 11991
pairs[:5], pairs[-5:]
([['go', 'va '],
['go', 'marche'],
['go', 'en route '],
['go', 'bouge '],
['hi', 'salut ']],
[['congratulations on your anniversary',
'flicitations pour ton anniversaire'],
['im studying electrical engineering', 'jtudie le gnie lectrique'],
['their relationship is deteriorating', 'leur relation se dtriore'],
['he studies computational linguistics',
'il tudie linformatique linguistique'],
['thirteen passengers were hospitalized',
'treize passagres furent hospitalises']])
ids = [0, 2, 5, 10, 40]
for i in ids:
print(f'id {i}, source: {source.index2word[i]}')
ids = [12, 22, 34, 11, 42]
for i in ids:
print(f'id {i}, target: {target.index2word[i]}')
id 0, source: SOS
id 2, source: go
id 5, source: who
id 10, source: hide
id 40, source: hunt
id 12, target: filez
id 22, target: baissezvous
id 34, target: commencez
id 11, target: file
id 42, target: aha
target.word2index['je'], source.word2index['i']
(40, 17)
target.word2count['suis'], source.word2count['am']
(1266, 144)
Tensors from sentences
def indexesFromSentence(lang, sentence):
return [lang.word2index[word] for word in sentence.split(' ')]
def tensorFromSentence(lang, sentence):
indexes = indexesFromSentence(lang, sentence)
indexes.append(EOS_token)
return torch.tensor(indexes, dtype=torch.long, device=device).view(-1, 1)
def tensorsFromPair(input_lang, output_lang, pair):
input_tensor = tensorFromSentence(input_lang, pair[0])
target_tensor = tensorFromSentence(output_lang, pair[1])
return (input_tensor, target_tensor)
sentence = pairs[1000][0]
l = source
for word in sentence.split(' '):
print(word, l.word2index[word])
he 85
is 295
old 296
in_t, out_t = tensorsFromPair(source, target, pairs[1000])
print(pairs[1000])
print(in_t)
print(out_t)
['he is old', 'il est vieux']
tensor([[ 85],
[295],
[296],
[ 1]])
tensor([[127],
[243],
[689],
[ 1]])
Encoder
class Encoder(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, input_dim, hidden_dim, embedding_dim, num_layers):
super(Encoder, self).__init__()
# set the encoder input dimension, embedding dimension,
# hidden dimesion, and number of layers
self.input_dim = input_dim
self.embedding_dim = embedding_dim
self.hidden_dim = hidden_dim
self.num_layers = num_layers
#initialize the embedding layer with input and embedding dimension
self.embedding = nn.Embedding(input_dim, self.embedding_dim)
# intialize the GRU to take the input dimension of embedding, and output
# dimension of hidden and set the number of gru layers
self.gru = nn.GRU(self.embedding_dim, self.hidden_dim,
num_layers=self.num_layers)
def forward(self, input, hidden):
embedded = self.embedding(input).view(1,1,-1)
outputs, hidden = self.gru(embedded, hidden)
return outputs, hidden
def init_hidden(self):
return torch.zeros(self.num_layers, 1, self.hidden_dim)
Decoder
class Decoder(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, output_dim, hidden_dim, embedding_dim, num_layers):
super(Decoder, self).__init__()
# set the encoder output dimension, embedding dimension,
# hidden dimension, and number of layers
self.embedding_dim = embedding_dim
self.hidden_dim = hidden_dim
self.output_dim = output_dim
self.num_layers = num_layers
# initialize every layer with the appropriate dimension.
# For the decoder layer, it will consist of an embedding,
# GRU, a Linear layer and a Log softmax activation function.
self.embedding = nn.Embedding(output_dim, self.embedding_dim)
self.gru = nn.GRU(self.embedding_dim, self.hidden_dim,
num_layers=self.num_layers)
self.out = nn.Linear(self.hidden_dim, output_dim)
self.softmax = nn.LogSoftmax(dim=1)
def forward(self, input, hidden):
# reshape the input to (1, batch_size)
input = input.view(1, -1)
embedded = F.relu(self.embedding(input))
output, hidden = self.gru(embedded, hidden)
prediction = self.softmax(self.out(output[0]))
return prediction, hidden
Let’s combine Encoder and Decoder into Seq2Seq
class Seq2Seq(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, encoder, decoder, device):
super().__init__()
# initialize the encoder and decoder
self.encoder = encoder
self.decoder = decoder
self.device = device
self.encoder_hidden = self.encoder.init_hidden().to(self.device)
def forward(self, source, target, teacher_forcing_ratio=0.5):
# get the input length (number of words in sentence)
input_length = source.size(0)
batch_size = source.shape[1] # target.shape[1]
target_length = target.shape[0]
vocab_size = self.decoder.output_dim
# initialize a variable to hold the predicted outputs
outputs = torch.zeros(target_length, batch_size,
vocab_size).to(self.device)
# encode every word in a sentence
encoder_hidden = self.encoder_hidden
for i in range(input_length):
encoder_output, encoder_hidden = self.encoder(source[i],
encoder_hidden)
# use the encoder’s hidden state as the decoder initial hidden state
decoder_hidden = encoder_hidden.to(device)
# add a token before the first predicted word
decoder_input = torch.tensor([SOS_token], device=device) # SOS
# topk is used to get the top K value over a list
# predict the output word from the current target word.
# If we enable the teaching force, then the #next decoder input is the
# next word, else, use the decoder output highest value.
for t in range(target_length):
decoder_output, decoder_hidden = self.decoder(decoder_input,
decoder_hidden)
outputs[t] = decoder_output
teacher_force = random.random() < teacher_forcing_ratio
topv, topi = decoder_output.topk(1)
decoder_input = (target[t] if teacher_force else topi)
if (teacher_force == False and decoder_input.item() == EOS_token):
break
return outputs
input_size, output_size
(6412, 11991)
embed_size = 256
hidden_size = 512
num_layers = 1
num_iteration = 2000 #50000
#create encoder-decoder model
encoder = Encoder(input_size, hidden_size, embed_size, num_layers)
decoder = Decoder(output_size, hidden_size, embed_size, num_layers)
model = Seq2Seq(encoder, decoder, device).to(device)
#print model
print(encoder)
print(decoder)
Encoder(
(embedding): Embedding(6412, 256)
(gru): GRU(256, 512)
)
Decoder(
(embedding): Embedding(11991, 256)
(gru): GRU(256, 512)
(out): Linear(in_features=512, out_features=11991, bias=True)
(softmax): LogSoftmax(dim=1)
)
Training this Seq2Seq model
teacher_forcing_ratio = 0.5
# Training step and return loss
def model_step(model, input_tensor, target_tensor, model_optimizer, criterion):
model_optimizer.zero_grad()
input_length = input_tensor.size(0)
loss = 0
epoch_loss = 0
output = model(input_tensor, target_tensor)
num_iter = output.size(0)
# calculate the loss from a predicted sentence with the expected result
for ot in range(num_iter):
loss += criterion(output[ot], target_tensor[ot])
loss.backward()
model_optimizer.step()
epoch_loss = loss.item() / num_iter
return epoch_loss
# Training Loop
def trainModel(model, source, target, pairs, num_iteration=20000):
model.train()
optimizer = optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=0.01)
criterion = nn.NLLLoss()
total_loss_iterations = 0
training_pairs = [tensorsFromPair(source, target, random.choice(pairs))
for i in range(num_iteration)]
for iter in range(1, num_iteration+1):
training_pair = training_pairs[iter - 1]
input_tensor = training_pair[0]
target_tensor = training_pair[1]
loss = model_step(model, input_tensor, target_tensor,
optimizer, criterion)
total_loss_iterations += loss
if iter % 500 == 0:
avarage_loss= total_loss_iterations / 5000
total_loss_iterations = 0
print('%d %.4f' % (iter, avarage_loss))
return model
model = trainModel(model, source, target, pairs, num_iteration)
500 0.5320
1000 0.5378
1500 0.5173
2000 0.5056
eng_eg, fra_eg = random.choice(pairs)
eng_eg, fra_eg
('youre pulling my leg', 'vous me faites marcher')
input_tensor = tensorFromSentence(source, eng_eg)
output_tensor = tensorFromSentence(target, fra_eg)
output = model(input_tensor, output_tensor)
output, output.shape
(tensor([[[-11.3427, -10.4012, -7.0340, ..., -11.0076, -10.9292, -11.4605]],
[[-10.7618, -5.5121, -6.3131, ..., -10.3156, -9.9775, -10.6938]],
[[-10.4780, -2.8254, -6.9759, ..., -10.1877, -9.8773, -10.3040]],
[[-10.3837, -1.0294, -8.0204, ..., -10.4328, -10.2545, -10.5195]],
[[-11.2248, -0.2836, -9.3885, ..., -11.3472, -11.3927, -11.4513]]],
grad_fn=<CopySlices>),
torch.Size([5, 1, 11991]))
output[0].topk(1)
torch.return_types.topk(
values=tensor([[-2.1347]], grad_fn=<TopkBackward0>),
indices=tensor([[127]]))
decoded_words = []
for ot in range(output.size(0)):
top_value, top_index = output[ot].topk(1)
if top_index[0].item() == EOS_token:
decoded_words.append('<EOS>')
break
else:
word = target.index2word[top_index[0].item()]
decoded_words.append(word)
print(top_index, word)
tensor([[127]]) il
tensor([[16]]) a
decoded_words
['il', 'a', '<EOS>']
Evaluate model predictions
def evaluate(model, input_lang, output_lang, sentences, max_length=MAX_LENGTH):
with torch.no_grad():
input_tensor = tensorFromSentence(input_lang, sentences[0])
output_tensor = tensorFromSentence(output_lang, sentences[1])
decoded_words = []
output = model(input_tensor, output_tensor, teacher_forcing_ratio=0)
for ot in range(output.size(0)):
topv, topi = output[ot].topk(1)
if topi[0].item() == EOS_token:
decoded_words.append('<EOS>')
break
else:
decoded_words.append(output_lang.index2word[topi[0].item()])
return decoded_words
def evaluateRandomly(model, source, target, pairs, n=10):
for i in range(n):
pair = random.choice(pairs)
print('source: {}'.format(pair[0]))
print('target: {}'.format(pair[1]))
output_words = evaluate(model, source, target, pair)
output_sentence = ' '.join(output_words)
print('predicted: {}'.format(output_sentence))
print('----')
evaluateRandomly(model, source, target, pairs)
source: the damage was done
target: le mal tait fait
predicted: il a <EOS>
----
source: where is the book
target: o est le livre
predicted: il a a <EOS>
----
source: tom scares me
target: tom me fait peur
predicted: tom a <EOS>
----
source: ive upset you
target: je vous ai contraries
predicted: il a a <EOS>
----
source: that would be fantastic
target: ce serait fantastique
predicted: il a a <EOS>
----
source: she has three kids
target: elle a trois enfants
predicted: il a a <EOS>
----
source: youre the oldest
target: cest toi lan
predicted: il a a <EOS>
----
source: im exhausted
target: je suis crev
predicted: je suis <EOS>
----
source: you look familiar
target: tu me dis quelquechose
predicted: il a a <EOS>
----
source: do you like pretzels
target: aimestu les bretzels
predicted: il a a <EOS>
----
Bahdanau Attention
Alignment Score
 $$
\text { score }{\text {alignment }} = W{\text {combined }} \cdot \tanh \left(W_{\text {decoder }} \cdot H_{\text {decoder }}+W_{\text {encoder }} \cdot H_{\text {encoder }}\right)
$$
$$
\text { score }{\text {alignment }} = W{\text {combined }} \cdot \tanh \left(W_{\text {decoder }} \cdot H_{\text {decoder }}+W_{\text {encoder }} \cdot H_{\text {encoder }}\right)
$$
$$ \text{Attention weights} = \text{Softmax}(\text{ score }_{\text {alignment}}) $$
class BahdanauDecoder(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, output_dim, hidden_dim, embedding_dim, num_layers):
super(BahdanauDecoder, self).__init__()
# set the encoder output dimension, embedding dimension,
# hidden dimension, and number of layers
self.embedding_dim = embedding_dim
self.hidden_dim = hidden_dim
self.output_dim = output_dim
self.num_layers = num_layers
# initialize every layer with the appropriate dimension.
# For the decoder layer, it will consist of an embedding,
# GRU, a Linear layer and a Log softmax activation function.
self.embedding = nn.Embedding(output_dim, self.embedding_dim)
# Apply alignment with 2 fully connected layer
# 1 after hidden and after encoder
self.fc_hidden = nn.Linear(self.hidden_dim, self.hidden_dim,
bias=False)
self.fc_encoder = nn.Linear(self.hidden_dim, self.hidden_dim,
bias=False)
self.weight = nn.Parameter(torch.FloatTensor(1, hidden_dim))
#concatenating context and decoder so hidden_dim*2
self.gru = nn.GRU(self.hidden_dim*2, self.hidden_dim,
num_layers=self.num_layers)
self.out = nn.Linear(self.hidden_dim, output_dim)
self.logsoftmax = nn.LogSoftmax(dim=1)
self.softmax = nn.Softmax(dim=1)
# forward will have encoder_outputs also
def forward(self, input, hidden, encoder_outputs):
encoder_outputs = encoder_outputs.squeeze()
# reshape the input to (1, batch_size)
input = input.view(1, -1)
embedded = F.relu(self.embedding(input))
# Calculating Alignment Scores
x = torch.tanh(self.fc_hidden(hidden)+
self.fc_encoder(encoder_outputs))
alignment_scores = x.bmm(self.weight.unsqueeze(2))
# Softmaxing alignment scores to get Attention weights
attn_weights = self.softmax(alignment_scores.view(1, -1))
# Multiplying the Attention weights with encoder outputs to get the context vector
context_vector = torch.bmm(attn_weights.unsqueeze(0),
encoder_outputs.unsqueeze(0))
# Concatenating context vector with embedded input word
output = torch.cat((embedded, context_vector), 2)
# Passing the concatenated vector as input to the LSTM cell
output, hidden = self.gru(output, hidden)
# Passing the GRU output through a Linear layer acting as a classifier
output = self.logsoftmax(self.out(output[0]))
return output, hidden, attn_weights
class Seq2SeqAttn(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, encoder, decoder, device):
super().__init__()
# initialize the encoder and decoder
self.encoder = encoder
self.decoder = decoder
self.device = device
self.encoder_hidden = self.encoder.init_hidden().to(self.device)
def forward(self, source, target, teacher_forcing_ratio=0.5):
# get the input length (number of words in sentence)
input_length = source.size(0)
batch_size = source.shape[1]
target_length = target.shape[0]
vocab_size = self.decoder.output_dim
# initialize a variable to hold the predicted outputs
outputs = torch.zeros(target_length, batch_size,
vocab_size).to(self.device)
# encode every word in a sentence
encoder_hidden = self.encoder_hidden
encoder_all_hidden = torch.zeros(input_length, self.encoder.hidden_dim,
device=self.device)
for i in range(input_length):
encoder_output, encoder_hidden = self.encoder(source[i],
encoder_hidden)
encoder_all_hidden[i, :] = encoder_hidden[0, 0]
# use the encoder’s hidden layer as the decoder initial hidden layer
decoder_hidden = encoder_hidden.to(device)
# add a token before the first predicted word
decoder_input = torch.tensor([SOS_token], device=device) # SOS
# topk is used to get the top K value over a list
# predict the output word from the current target word.
# If we enable the teaching force, then the #next decoder input is the
# next word, else, use the decoder output highest value.
for t in range(target_length):
decoder_output, decoder_hidden, attn_weights = self.decoder(decoder_input,
decoder_hidden, encoder_all_hidden)
outputs[t] = decoder_output
teacher_force = random.random() < teacher_forcing_ratio
topv, topi = decoder_output.topk(1)
decoder_input = (target[t] if teacher_force else topi)
if (teacher_force == False and decoder_input.item() == EOS_token):
break
return outputs
embed_size = 256
hidden_size = 256
num_layers = 1
num_iteration = 2000 #100000
#create encoder-decoder model
encoder = Encoder(input_size, hidden_size, embed_size, num_layers)
decoder = BahdanauDecoder(output_size, hidden_size, embed_size, num_layers)
model = Seq2SeqAttn(encoder, decoder, device).to(device)
print(encoder), print(decoder)
Encoder(
(embedding): Embedding(6412, 256)
(gru): GRU(256, 256)
)
BahdanauDecoder(
(embedding): Embedding(11991, 256)
(fc_hidden): Linear(in_features=256, out_features=256, bias=False)
(fc_encoder): Linear(in_features=256, out_features=256, bias=False)
(gru): GRU(512, 256)
(out): Linear(in_features=256, out_features=11991, bias=True)
(logsoftmax): LogSoftmax(dim=1)
(softmax): Softmax(dim=1)
)
(None, None)
model = trainModel(model, source, target, pairs, num_iteration)
500 0.5050
1000 0.5387
1500 0.5152
2000 0.5034
evaluateRandomly(model, source, target, pairs)
source: youll like this
target: vous allez aimer ceci
predicted: cest a <EOS>
----
source: i wrote this book
target: jai crit ce livre
predicted: je suis <EOS>
----
source: she teased him
target: elle le taquina
predicted: cest <EOS>
----
source: tom was shouting
target: tom hurlait
predicted: tom a a
----
source: got it
target: aha
predicted: cest a <EOS>
----
source: i have forgotten
target: jai oubli
predicted: je suis <EOS>
----
source: youre still young
target: vous tes encore jeunes
predicted: vous tes <EOS>
----
source: i killed the mosquito
target: jai tu le moustique
predicted: je suis <EOS>
----
source: i believe in ghosts
target: je crois aux fantmes
predicted: je suis <EOS>
----
source: whats it used for
target: quoi cela sertil
predicted: cest a <EOS>
----