Message Passing in Graph Conv Network
Posted on * • 3 minutes • 563 words
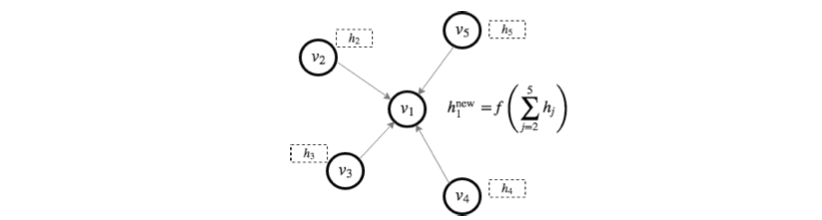
Message Passing
Its an iterative scheme of updating node representations based on the aggregation from nearby nodes.
Suppose $h_{u}^{k}$ represents the node embeddings for some node at iteration $k$, then at $k+1$, the following was orginally proposed for GNN
$ h_{u}^{(k+1)} = σ (W_{self}^{k+1} h_{u}^{k} + W_{neigh}^{k+1} Σ_{neigh} h_{v}^{k}) $
Collapsing $W_{self}$ and $W_{neigh}$ by adding self-loops to Adjacency matrix:
$ H^{(k+1)} = σ (W^{k+1}(A + I) H^{k} ) $
Coming from GCN perspective, Kipf and Welling 2016, proposed follwing: $ H^{(k+1)} = σ (W^{k+1}\hat{A} H^{k}) $
where, $ \hat{A} = (D+I)^{-1/2}(I+A)(D+I)^{-1/2} $ that Normalizes $A$ by # of nodes in neighborhood and $D$ is the degree matrix
Lets look at it with code
import numpy as np
import networkx as nx
from scipy.linalg import sqrtm
# Adjacencey matrix
A = np.array(
[[0, 0, 1, 0, 1],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 1],
[0, 0, 0, 1, 1],
[0, 0, 1, 0, 1],
[1, 1, 0, 0, 0]]
)
g = nx.from_numpy_array(A)
A_tilde = A + np.eye(g.number_of_nodes())
A_tilde
array([[1., 0., 1., 0., 1.],
[0., 1., 0., 0., 1.],
[0., 0., 1., 1., 1.],
[0., 0., 1., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 0., 0., 1.]])
D_tilde = np.zeros_like(A_tilde)
np.fill_diagonal(D_tilde, np.asarray(A_tilde.sum(axis=1)).flatten())
D_tilde_invroot = np.linalg.inv(sqrtm(D_tilde))
D_tilde_invroot
array([[0.57735027, 0. , 0. , 0. , 0. ],
[0. , 0.70710678, 0. , 0. , 0. ],
[0. , 0. , 0.57735027, 0. , 0. ],
[0. , 0. , 0. , 0.57735027, 0. ],
[0. , 0. , 0. , 0. , 0.57735027]])
A_hat = D_tilde_invroot @ A_tilde @ D_tilde_invroot
A_hat
array([[0.33333333, 0. , 0.33333333, 0. , 0.33333333],
[0. , 0.5 , 0. , 0. , 0.40824829],
[0. , 0. , 0.33333333, 0.33333333, 0.33333333],
[0. , 0. , 0.33333333, 0.33333333, 0.33333333],
[0.33333333, 0.40824829, 0. , 0. , 0.33333333]])
Implement GCN using Pytorch
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
import torch.optim as optim
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
class GCNLayer(nn.Module):
"""
GCN layer
Args:
input_dim (int): Dimension of the input
output_dim (int): Dimension of the output (a softmax distribution)
A (torch.Tensor): 2D adjacency matrix
"""
def __init__(self, input_dim: int, output_dim: int, A: torch.Tensor):
super(GCNLayer, self).__init__()
self.input_dim = input_dim
self.output_dim = output_dim
self.A = A
# A_hat = A + I
self.A_hat = self.A + torch.eye(self.A.size(0))
# Create diagonal degree matrix D using another way
self.ones = torch.ones(input_dim, input_dim)
self.D = torch.matmul(self.A.float(), self.ones.float())
# Extract the diagonal elements
self.D = torch.diag(self.D)
# Create a new tensor with the diagonal elements and zeros elsewhere
self.D = torch.diag_embed(self.D)
# Create D^{-1/2}
self.D_neg_sqrt = torch.diag_embed(torch.diag(torch.pow(self.D, -0.5)))
# Initialise the weight matrix as a parameter
self.W = nn.Parameter(torch.rand(input_dim, output_dim))
def forward(self, X: torch.Tensor):
# D^-1/2 * (A_hat * D^-1/2)
support_1 = torch.matmul(self.D_neg_sqrt, torch.matmul(self.A_hat, self.D_neg_sqrt))
# (D^-1/2 * A_hat * D^-1/2) * (X * W)
support_2 = torch.matmul(support_1, torch.matmul(X, self.W))
# ReLU(D^-1/2 * A_hat * D^-1/2 * X * W)
H = F.relu(support_2)
return H
# Example Usage
input_dim = 3 # Assuming the input dimension is 3
output_dim = 2 # Assuming the output dimension is 2
# Example adjacency matrix
A = torch.tensor([[1., 0., 0.],
[0., 1., 1.],
[0., 1., 1.]])
# Create the GCN Layer
gcn_layer = GCNLayer(input_dim, output_dim, A)
# Example input feature matrix
X = torch.tensor([[1., 2., 3.],
[4., 5., 6.],
[7., 8., 9.]])
# Forward pass
output = gcn_layer(X)
print("Otput Feat", output)
Otput Feat tensor([[ 8.4075, 2.2147],
[18.6713, 4.6855],
[21.7627, 5.4416]], grad_fn=<ReluBackward0>)